How Iron Dysregulation Fuels Metabolic Disease
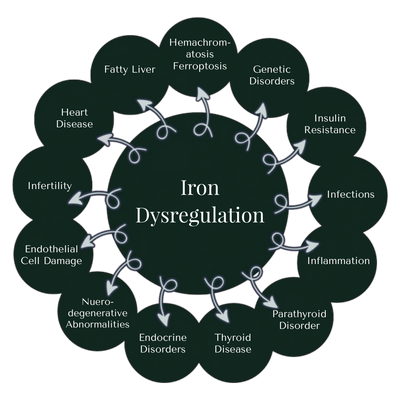
Iron is essential for life. It plays a central role in oxygen transport (via hemoglobin), energy production (in the mitochondria), DNA synthesis, and immune defense. Without adequate iron, cells cannot produce energy efficiently or maintain healthy function—leading to fatigue, weakness, and impaired immunity.
But while iron is vital, it must be carefully regulated. When iron accumulates beyond safe levels, free ferrous iron (Fe²⁺) reacts with hydrogen peroxide in the Fenton reaction, producing hydroxyl radicals—among the most damaging free radicals known. These radicals attack lipids, proteins, and DNA, causing widespread oxidative stress.
This oxidative injury triggers chronic inflammation in the liver, muscles, and fat tissue. The damage impairs insulin receptor signaling and reduces glucose uptake, pushing the body toward insulin resistance. Over time, this cascade contributes to fatty liver, impaired metabolism, and type 2 diabetes—hallmarks of metabolic syndrome.
Iron is essential, but like fire, it must be contained. Understanding and managing iron balance is critical to maintaining metabolic health and preventing chronic disease.
Key Highlights:
- Fenton Chemistry: Excess Fe²⁺ + H₂O₂ → hydroxyl radicals → oxidative injury
- Inflammation Loop: High ROS → cytokine release → further iron sequestration (via hepcidin)
- Insulin Signaling Block: Oxidative damage to insulin receptor pathways → impaired glucose uptake
- Clinical Impact: Correlation between elevated ferritin levels and metabolic syndrome risk

The Hidden Mechanism Behind Cellular and Systemic Damage

Iron overload, or hemochromatosis, is far more than a storage disorder—it is a silent biochemical trigger of ferroptosis, the iron-dependent cell death pathway now recognized as a root mechanism in neurodegeneration, liver disease, autoimmune conditions, and autism spectrum disorders. Ferroptosis arises when free iron catalyzes lipid peroxidation in the context of glutathione depletion and antioxidant failure.
The Equation
Iron Overload (Hemochromatosis) = Ferroptosis = Cellular Collapse
Mechanistic Breakdown
Ferroptosis requires three main components:
- Free ferrous iron (Fe²⁺) – catalyzes the Fenton reaction, generating hydroxyl radicals
- Polyunsaturated lipids – highly oxidizable components of cell membranes
- Glutathione deficiency – impairs GPX4, the enzyme responsible for neutralizing lipid peroxides
In iron overload:
- Non-transferrin-bound iron (NTBI) increases
- Intracellular iron accumulates in mitochondria, brain, liver, and heart
- Glutathione is rapidly consumed under oxidative stress
- Ferroptosis is triggered, causing functional collapse of affected tissues
Consequences of Iron-Driven Ferroptosis
- Brain: Iron accumulation in the basal ganglia and cortex leads to neurodegeneration, autism, and Alzheimer’s.
- Liver: Hepatic iron overload results in steatosis, cirrhosis, and fibrosis.
- Pancreas: Islet iron toxicity contributes to insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes.
- Heart: Myocardial iron deposits can cause cardiomyopathy and arrhythmias.
- Joints: Iron deposition in synovial tissue promotes arthritis and joint degeneration.
- Skin: Iron-driven oxidative stress leads to hyperpigmentation and collagen breakdown.
Glucoferrin®: The Only Biochemical Antidote
Glucoferrin® is the only therapeutic compound known to:
- Regulate iron metabolism and neutralize labile iron without causing anemia.
- Restore sulfur-driven antioxidant capacity, replenishing glutathione via cysteine, methionine, and taurine.
- Reactivate GPX4 and SLC7A11 pathways to suppress lipid peroxidation.
- Protect mitochondria, liver, and brain cells from oxidative collapse.
Iron overload equals ferroptosis. Glucoferrin® is the first and ONLY solution that targets this mechanism upstream—restoring balance, protecting life, and preventing irreversible degeneration.